Cancer: Overview, causes, treatments, and types
When you find out you have cancer, it can be overwhelming and stressful. Knowing what to expect from diagnosis to recovery can boost your confidence and assist you in taking control of your health. This is a general explanation of what is cancer? what symptoms to look for, how it is found, treatments, and follow-up care.
Overview
What is cancer?
Malignant growth is an enormous gathering of illnesses with one thing in like manner: They all happen when ordinary cells become malignant cells that duplicate and spread.
In the United States, cancer is the second leading cause of death, but its incidence is declining compared to 20 years ago. Early location and imaginative therapies are relieving malignant growth and assisting individuals with disease live longer. To aid in the prevention of cancer, medical researchers are simultaneously identifying independent risk factors linked to the disease.
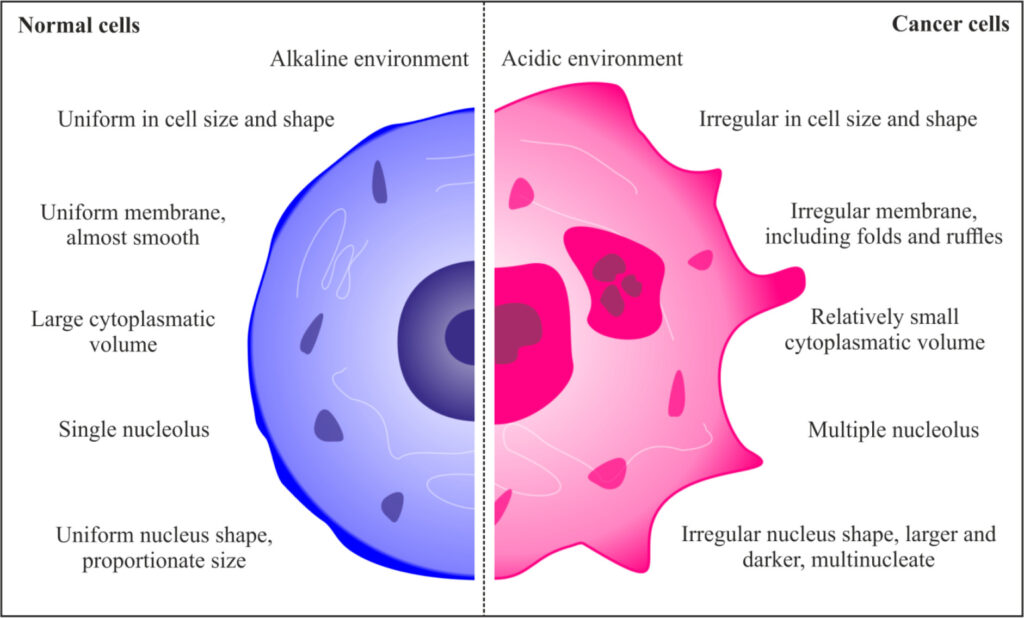
What distinguishes a cancerous cell from a normal cell?
Genes normally give cells instructions to follow. Cells are instructed by genes when to begin and when to stop growing. Normal cell rules are broken by cancerous cells:
• Customary cells parcel and copy in a controlled manner. Cancerous cells can’t stop growing.
• Apoptosis is programmed into normal cells. Carcinogenic cells overlook those headings.
• The cells that make up solid organs stay put. All malignant cells can move around.
•Typical cells don’t develop as quick as harmful cells.
How does cancer start in your body?
When one or more genes mutate and produce cancerous cells, cancer develops. Tumor clusters are formed by these cells. Cancerous cells can break free from tumors and travel to other parts of your body through your lymphatic system or bloodstream. (This is what doctors call a metastasis.)
A breast tumor, for instance, may progress to your lungs and make it difficult to breathe. When you have some kinds of blood cancer, abnormal cells in your bone marrow make abnormal blood cells that multiply out of control. The abnormal cells eventually outnumber the normal blood cells-What is Cancer?
How common is cancer?
- The American Cancer Society says that one in two men and one in three women and people who were assigned a gender at birth (AFAB) will get cancer. Starting around 2019, more than 16.9 million individuals in the U.S. were living with disease. In the United States, these cancers(What is Cancer?) are the most prevalent:
- Cancer of the breast: The most prevalent form of cancer is breast cancer. It mostly affects AFAB people and women. However, men and AMAB are affected by about 1% of all cases of breast cancer.
- Cellular breakdown in the lungs: Cellular breakdown in the lungs is the second most normal disease. There are two sorts of cellular breakdown in the lungs: non-little cell malignant growth and little cell cellular breakdown in the lungs.
- Cancer of the prostate: This disease influences 1 out of 9 men and individuals AMAB.
- Cancer of the colon: Different parts of your digestive system can be affected by colon cancer and rectal cancer.
- Cancers of the blood: Blood cancers like lymphoma and leukemia are the most common.
- Who’s impacted by malignant growth?
- Cancer can affect almost anyone, but data show that cases vary depending on race and sex. As per the 2022 Yearly Report on Malignant growth, the infection:
- What is Cancer?
• Affects men and people with AMAB slightly more than women and people with AFAB.
• Is more prevalent in Black men (AMAB) than in other racial groups.
• Affects more Alaska Native and American Indian women (AFAB) than other racial groups.
Cancer can affect anyone, but most often affects people 60 and older-What is Cancer?
Symptoms and Causes
What are cancer symptoms?
Malignant growth is a convoluted illness. You can have disease for a really long time without creating side effects. In other instances, cancer may cause observable symptoms that rapidly deteriorate. Numerous cancer symptoms are similar to those of other, less serious diseases. Having specific side effects doesn’t mean you have malignant growth. As a general rule, you ought to converse with a medical care supplier whenever there’s an adjustment of your body that goes on for over about fourteen days.
Breast cancer awareness
First symptoms of cancer
Some normal early disease side effects include:
• Unpredictable weight loss
•Ongoing sleepiness.
• Chronic pain.
• a fever that typically occurs at night
• Changes in the skin, particularly new moles or moles that change shape and size.
Cancer can cause additional symptoms if it is not treated, such as:
• Easier bruising or bleeding-What is Cancer?
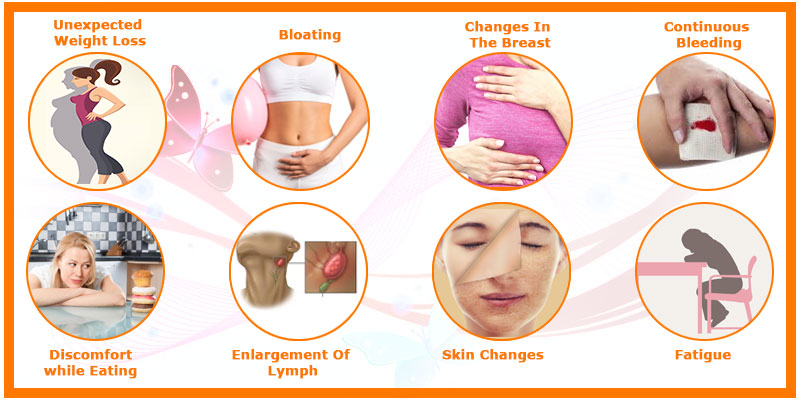
•Protuberances or knocks under your skin that don’t disappear.
•Trouble relaxing.
• Trouble swallowing
What causes cancer? What is Cancer?
A genetic condition is cancer. It happens when qualities that oversee cell action change and make unusual cells that separation and duplicate, ultimately disturbing how your body works.
Analysts in the clinical field gauge that acquired hereditary changes over which you have no control represent 5% to 12% of all diseases.
The majority of the time, cancer is brought on by an acquired genetic mutation. Throughout your life, hereditary changes that you have obtained happen. Medical researchers have identified numerous risk factors that increase your risk of developing cancer.
Cancer risk factors you can control
• Vamping: Lung, pancreatic, esophageal, and oral malignant growth are bound to happen in individuals who smoke cigarettes, stogies, and e-cigarettes.
•Diet: It is possible to increase your risk of developing a variety of cancers by consuming foods high in fat or sugar. In the event that you don’t practice enough, you’re likewise bound to become ill.
• Conditions: Asbestos, pesticides, and radon are instances of natural poisons that can ultimately cause disease.
•Radiation openness: The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation significantly raises your risk of skin cancer. Treatment with too much radiation can also increase the risk.
• Chemical treatment: Bosom and endometrial disease might be more normal in AFAB ladies and that taking chemical substitution treatment.
How can I lower my chance of getting cancer?
You can decrease your gamble by changing a portion of your way of life decisions:
• Make an effort to quit using tobacco or smoking. Get some information about smoking discontinuance programs that can assist you with stopping tobacco.
• Adhere to an eating regimen that is great for you. If you need help controlling your weight, talk to your doctor about weight management programs and nutritional advice-What is Cancer?
• Include daily exercise in your routine. Your immune system may be strengthened by exercise, improving its ability to fight cancer.
• Avoid poisons like pesticides, asbestos, and radon.
• Take precautions against sunburn.
•Have ordinary disease screenings.
Diagnosis and Tests
How do healthcare providers diagnose cancer?
Medical services suppliers start a malignant growth finding by doing an extensive actual assessment. They will inquire about your symptoms. They might get some information about your family clinical history. Additionally, they may take the following tests:
• Blood tests
•Imaging tests.
• Embryos.
Blood tests
Cancer blood tests may include:
• CBC (complete blood count): Your blood cells are counted and measured in a CBC test.
• Signs of cancer: Substances that are released by cancer cells or by your normal cells in response to cancer cells are known as tumor markers.
• Tests for blood proteins: Medical care suppliers utilize an interaction called electrophoresis to quantify immunoglobulin’s. Immunoglobulins are produced when certain cancers are detected by your immune system.
•Circling cancer cell tests: Tumors that have cancer may shed cells. The activity of cancer can be monitored by healthcare providers by tracking tumor cells.
What is the best pain relief for lower back pain?
Imaging tests
• Scans using computer tomography (CT): CT filters check for harmful cancers’ area and effect on your organs and bones.
•X-rays: X-beams utilize safe measures of radiation to make pictures of your bones and delicate tissues.
•Positron emanation test (PET) filter: PET outputs produce pictures of your organs and tissues at work. This test could be used by medical professionals to find early signs of cancer.
• Solography: High-intensity sound waves are used in an ultrasound to show your body’s structures.
• Imaging by magnetic resonance (MRI): Images of your organs and other body structures are created by MRIs using a large magnet, radio waves, and a computer.
• Meta-iodobenzylguanidine of iodine (MIGB): Carcinoid tumors and neuroblastoma are examples of cancers that can be detected with this nuclear imaging test.
Biopsies
A biopsy is a procedure performed by medical professionals to obtain cells, tissue, fluid, or growths for microscope examination. There are a few sorts of biopsies:
• Biopsy by needle: A fine needle aspiration or a fine needle biopsy is two names for this procedure. To remove cells, fluid, or tissue from suspicious lumps, healthcare professionals use a thin, hollow needle and syringe. Needle biopsies are frequently finished to assist with diagnosing bosom malignant growth, thyroid disease or disease in your lymph hubs.
• Skin biopsies: A small amount of your skin is removed by healthcare professionals to diagnose skin cancer-What is Cancer?
• A bone marrow biopsy: To check for indications of illness, remembering malignant growth for your bone marrow, medical care suppliers take a little example of your bone marrow.
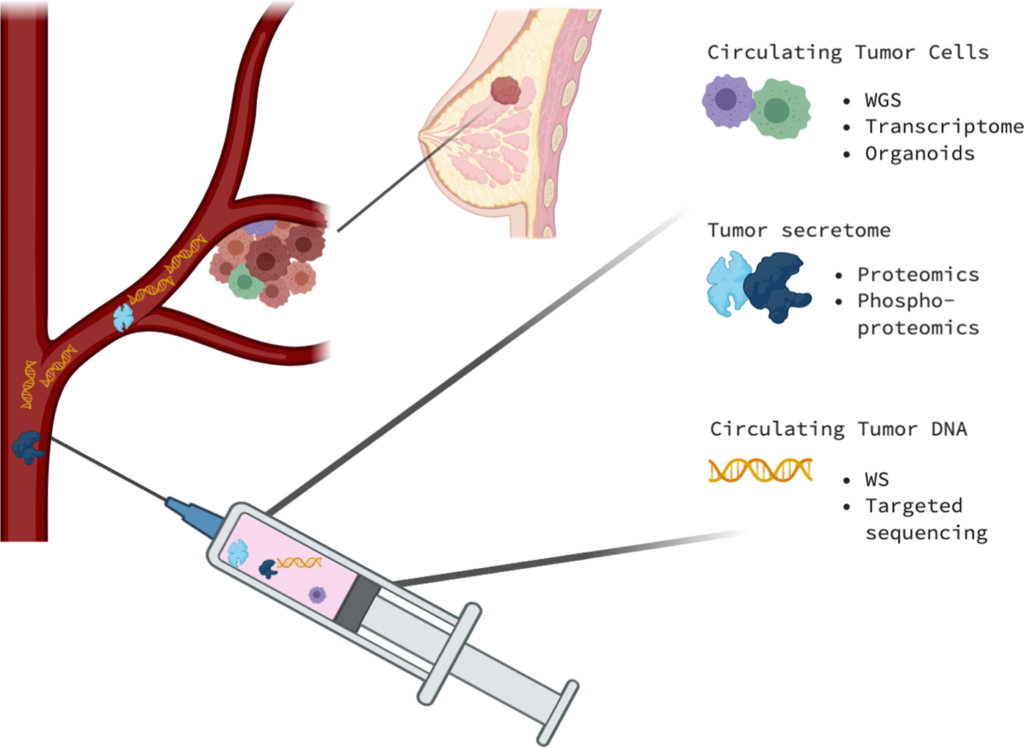
•Biography via endoscope or laparoscope: For these biopsies, an endoscope or laparoscope is used to look inside your body.. An instrument is inserted through a small cut in your skin in either of these approaches. An endoscope is a slim, adaptable cylinder with a camera on the tip, alongside a slicing device to eliminate your example. A laparoscope is a somewhat unique degree.
• Biopsy through an incision or excision: For these open biopsies, a specialist cuts into your body and either the whole growth is taken out (excisional biopsy) or a piece of the cancer is eliminated (incisional biopsy) to test or treat it.
•Perioperative biopsy: A frozen section biopsy may be the name given to this test. This biopsy takes place simultaneously with another procedure. Your tissue will be taken out immediately and tested. If you require treatment, it can begin immediately because the results will be available shortly after the procedure.
Genetic testing
Cancer can result from mutations in a single gene or multiple genes that work together. Cancer has been linked to more than 400 genes, according to researchers. Malignant growth chance might be higher in individuals who acquire these qualities from their natural guardians. Medical care suppliers might suggest hereditary testing for malignant growth assuming you have an acquired type of disease. They might also conduct genetic testing in order to develop cancer-specific therapy. They use test results to foster a finding. Your diagnosis will be given a number or stage by them. The higher the number, the more disease has spread.
How is cancer stage determined?
Medical services suppliers use disease organizing frameworks to design therapy and foster a guess or anticipated result. The most widely used method of cancer staging is TNM. T represents essential growth. The letter N denotes whether or not a tumor has spread to your lymph nodes. The word “metastasis” refers to the spread of cancer..
What are the four phases of malignant growth?
There are four stages to most cancers. The tumor’s size and location, among other factors, determine the specific stage:
• Phase I: The malignant growth is restricted to a little region and hasn’t spread to lymph hubs or different tissues.
• Phase II: Despite its growth, the cancer has not spread.
•Stage III: The disease has become bigger and has conceivably spread to lymph hubs or different tissues.
• Stage four: The disease has spread to different organs or region of your body. This stage is additionally alluded to as metastatic or high level malignant growth.
There is a Stage 0 in addition to the more common stages one through four. This earliest stage depicts disease that is as yet confined to the area wherein it began. The majority of healthcare providers classify cancers that are still in Stage 0 as pre-cancerous because they typically require little or no treatment.
Management and Treatment
How do medical care suppliers treat disease?
Depending on your situation, healthcare providers may employ multiple treatments, sometimes combining them. Normal malignant growth medicines include:
• Chemical therapy: Chemotherapy is one of the most widely recognized disease medicines. It kills cancer cells with potent drugs. Chemotherapy can be administered intravenously (via a needle into a vein) or as a pill. Providers may be able to direct chemotherapy to the affected area in some instances.
•Radiation treatment: This therapy kills disease cells with high measurements of radiation. Your doctor might give you chemotherapy and radiation therapy at the same time.

• Procedure: Surgical removal of cancerous tumors that have not spread is an option. Your medical care supplier might suggest treatment. This treatment combines surgery with chemotherapy or radiation to either kill cancer cells that may remain after surgery or shrink a tumor prior to surgery.
• Hormone treatment: Providers may occasionally prescribe hormones that inhibit other hormones that cause cancer. For instance, men and individuals relegated male upon entering the world who have prostate malignant growth could get chemicals to keep testosterone (which adds to prostate disease) lower than expected.
• Therapy that alters the biological response: This treatment invigorates your resistant framework and assists it with performing all the more really. By altering your body’s natural processes, it accomplishes this.
• Cancer immunotherapy: Immunotherapy is a malignant growth treatment that connects with your insusceptible framework to battle the sickness. Biotherapy may be used to describe the treatment.
• Cancer treatment that is specific: A cancer treatment known as targeted therapy focuses on the genetic changes or mutations that transform normal cells into cancer cells-What is Cancer?.
•Bone marrow relocates: This treatment, also known as stem cell transplantation, involves replacing diseased stem cells with healthy ones. Autologous transplantation utilizes your stock of solid undifferentiated organisms. In allogeneic transplantation, donor stem cells are utilized.
What are cancer treatment side effects?
Medical care suppliers work to adjust the therapy so it annihilates malignant growth without destructive or enduring aftereffects. All things considered, all malignant growth medicines make side impacts. After completing some treatments, side effects can persist for years. Many individuals benefit from palliative consideration that facilitates disease side effects and treatment aftereffects. The most common side effects of treating cancer are:
• Illness.
•Queasiness and retching.
• Weariness
•Pain.
Outlook / Prognosis
What is cancer’s outlook and prognosis?
This moment, more individuals are being restored of disease or living longer with malignant growth. By and large, individuals with disease that were analyzed and treated before it could spread have a decent standpoint.
However, just as your cancer prognosis is unique, so are you? Your healthcare providers will use the following factors to determine your prognosis:
• Your general well-being-What is Cancer?
• The sort of disease that you have
• How far along your cancer is.
• How your response to treatment might be.
• Your prognosis is influenced by your overall health, the stage of your cancer, the type of cancer you have, and how well you respond to treatment.
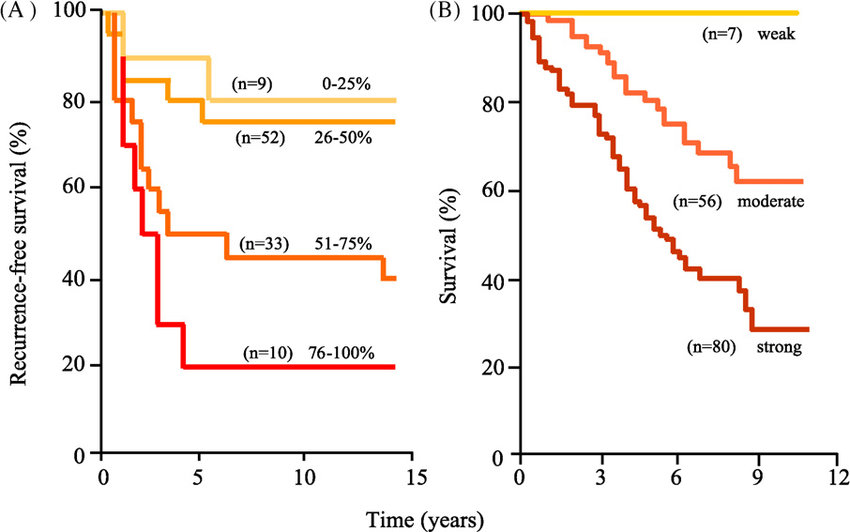
What are cancer survival rates?
Estimates of survival rates are based on the experiences of a large number of people with various types of cancer. Cancer survival rates differ based on the type, stage, and treatment of the disease, just as prognoses do. As per the latest information from the Public Malignant growth Establishment, 68% of individuals with any sort of disease were alive five years after their conclusion.
Living With
How do I live with cancer?
- Taking care of oneself is an essential part of living with cancer. Some suggestions for self-care include:
- Lay out great eating and exercise propensities. For healthy menu ideas, contact a nutritionist.
- A frequent symptom and treatment side effect is fatigue. Rest when you need to, not just when you can, and pay attention to your body.
- You might have cancer for a very long time. That is uplifting news, obviously, yet ongoing sickness might challenge. Conversing with an emotional well-being proficient or finding a care group might assist you with exploring difficulties.
What is cancer survivorship?
In the event that you have disease, you are a malignant growth survivor. After receiving a cancer diagnosis, survivorship begins and lasts for the rest of your life. As a cancer survivor, you are likely to face numerous difficulties or issues-What is Cancer?.
Cancer that comes back
Treatment for cancer does not always get rid of all the cancer cells. Those cells may develop into new malignant tumors. Malignant growth that returns, or repetitive disease, may show up at similar spot as the first disease, in neighboring lymph hubs or spread to organs and tissues far away from the first site.

Second cancer
A subsequent disease is another malignant growth. Individuals who have second diseases might have malignant growth in a similar organ or region of their body as the primary malignant growth, yet it’s an alternate sort of malignant growth from what it was previously. They may likewise have disease in various regions of their bodies. As more people with cancer live longer, second cancers are becoming more common..
Cancer fatigue
Cancer fatigue is an overwhelming feeling of fatigue that doesn’t get better with more sleep. After finishing treatment, some cancer patients experience chronic fatigue.
Cancer pain-What is Cancer?
Some disease medicines have enduring incidental effects that might cause torment. One investigation discovered that 39% of individuals who finished disease therapy had constant torment. One example of pain that may not go away even after treatment is peripheral neuropathy.
Chemotherapy brain fog
Chemotherapy mind haze (chemo cerebrum) happens when disease or malignant growth treatment influences your memorable capacity or follow up on data. About 75% of cancer patients tell their doctors and nurses that they have(What is Cancer?) trouble remembering, staying focused, and finishing things.
When should I see my healthcare provider?
Talk to your doctor about any problems you have while you are being treated for cancer. Call your oncology group in the event that you notice:
• a fever that is at least 101 degrees Fahrenheit (38.33 degrees Celsius).
• Serious headaches
•Chills-What is Cancer?
• Constant cough
• Dyspnea, or breathlessness
• Infections of the mouth or lips
• A sudden loss of more than five pounds
• Excessive vomiting (three times per hour for at least three hours).
• Blood in your feces or urine (poop)
•Extreme draining or swelling.(What is Cancer?)
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider?
Power is knowledge. If you’ve been told you have cancer, you need as much information as you can get your hands on. The following are some inquiries you should make to your doctor-What is Cancer?

• What kind of cancer am I fighting?
•Has the malignant growth spread to different region of my body?
•Is my disease hereditary?(What is Cancer?)
• How likely am I to survive?
• Which treatments would you suggest?
•What are the dangers and advantages of my treatment?
•What amount of time will treatment require?
•Can I work during disease treatment?
• Will my treatment for cancer affect my fertility?
•Will I really want to remain in the clinic for my treatment?
• Could I profit from partaking in a clinical preliminary?(What is Cancer?)
A note from Cleveland Clinic
The words “you have malignant growth” might be perhaps of the hardest thing anybody needs to hear. When you find out that you have cancer, you might feel scared and overwhelmed. There are a lot of people who think they’ve lost control of their lives. Your medical professionals are aware of all of those emotions. They are aware that getting cancer is a life-altering event.(What is Cancer?) They likewise know malignant growth treatment is a distressing excursion. Know that your healthcare providers will be by your side every step of the way if you have cancer.
Thanks for best reply